astm tear testing|rubber tear strength test : supplier 5.1 Vulcanized rubber and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) often fail in service due to the generation and propagation of a special type of rupture called a tear. This test method measures the resistance to tearing action. Can I autoclave Triton ® X-100, Product 234729? Triton X-100 solutions are stable to autoclaving. At certain concentrations, the solutions may be cloudy but dispersible above the cloud point. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Installer une clôture en bois est simple grâce à un socle, parfois autoclave, qui retient la palissade au sol. Pour cela, il faut également creuser un trou et y faire couler du béton. Dans cette dalle, fixez le socle sur lequel installer ensuite le .
5.1 Vulcanized rubber and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) often fail in service .ASTM D624 is a common test method used to determine the tear strength of vulcanized rubber and thermoplastic elastomers. Due to the specimen shapes often used, this test is sometimes called a trouser, angle, or crescent test. 5.1 Vulcanized rubber and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) often fail in service due to the generation and propagation of a special type of rupture called a tear. This test method measures the resistance to tearing action.ASTM's fatigue and fracture standards provide the appropriate procedures for carrying out fatigue, fracture, and other related tests on specified materials. These tests are conducted to examine and evaluate the behavior, susceptibility, and extent of resistance of certain materials to sharp-notch tension, tear, axial fatigue, strain-controlled .
Type C (right angle) test piece, divided by the thickness of the test piece.3.2.4 Type T or trouser tear strength—the mean or median force, calculated in accordance with procedures in this method, required to propagate a tear.ASTM's physical and mechanical testing standards provide guides for the proper procedures employed in the determination of the physical, mechanical, and metallographic properties of certain materials, particularly metals and alloys.
1.1 This test method covers the dynamic tear (DT) test using specimens that are 3⁄16 in. to 5⁄8 in. (5 mm to 16 mm) inclusive in thickness. 1.2 This test method is applicable to materials with a minimum thickness of 3⁄16 in. (5 mm).A tearing resistance tester is specifically designed to measure the force required to propagate a tear in a sample material. This measurement is crucial for determining the durability and suitability of materials under real-world conditions.Tear testing is a mechanical testing procedure used to measure a material’s resistance to tearing. It involves applying a controlled force to a specimen, often with a pre-initiated tear or cut, to evaluate how the material behaves under conditions that might lead to tearing.Scope. 1.1 This test method covers the dynamic tear (DT) test using specimens that are 3⁄16 in. to 5⁄8 in. (5 mm to 16 mm) inclusive in thickness. 1.2 This test method is applicable to materials with a minimum thickness of 3⁄16 in. (5 mm).
The Tongue Tear Test (ASTM D2261) is an essential technique for evaluating the tearing strength of textiles and offers insightful data regarding their resilience to tearing across a range of industries.
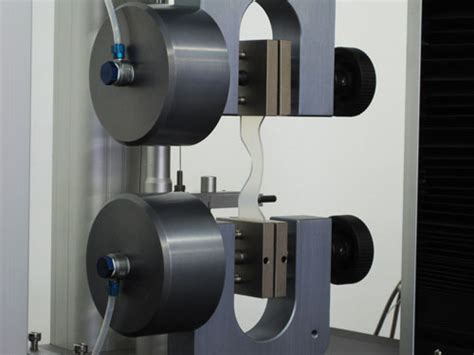
vulcanized rubber tear test
ASTM D624 is a common test method used to determine the tear strength of vulcanized rubber and thermoplastic elastomers. Due to the specimen shapes often used, this test is sometimes called a trouser, angle, or crescent test. 5.1 Vulcanized rubber and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) often fail in service due to the generation and propagation of a special type of rupture called a tear. This test method measures the resistance to tearing action.ASTM's fatigue and fracture standards provide the appropriate procedures for carrying out fatigue, fracture, and other related tests on specified materials. These tests are conducted to examine and evaluate the behavior, susceptibility, and extent of resistance of certain materials to sharp-notch tension, tear, axial fatigue, strain-controlled .Type C (right angle) test piece, divided by the thickness of the test piece.3.2.4 Type T or trouser tear strength—the mean or median force, calculated in accordance with procedures in this method, required to propagate a tear.
ASTM's physical and mechanical testing standards provide guides for the proper procedures employed in the determination of the physical, mechanical, and metallographic properties of certain materials, particularly metals and alloys.
1.1 This test method covers the dynamic tear (DT) test using specimens that are 3⁄16 in. to 5⁄8 in. (5 mm to 16 mm) inclusive in thickness. 1.2 This test method is applicable to materials with a minimum thickness of 3⁄16 in. (5 mm).
A tearing resistance tester is specifically designed to measure the force required to propagate a tear in a sample material. This measurement is crucial for determining the durability and suitability of materials under real-world conditions.
tear strength test method
tear initiation strength test
rubber tear strength test
Tear testing is a mechanical testing procedure used to measure a material’s resistance to tearing. It involves applying a controlled force to a specimen, often with a pre-initiated tear or cut, to evaluate how the material behaves under conditions that might lead to tearing.Scope. 1.1 This test method covers the dynamic tear (DT) test using specimens that are 3⁄16 in. to 5⁄8 in. (5 mm to 16 mm) inclusive in thickness. 1.2 This test method is applicable to materials with a minimum thickness of 3⁄16 in. (5 mm).
describe autoclaving process
describe the use of an autoclave in microbiology laboratory
Celles-ci ont besoin d’un environnement dépourvu d’oxygène (anaérobie) pour germer puis proliférer, ce qui explique que le botulisme soit principalement lié à des conserves .
astm tear testing|rubber tear strength test